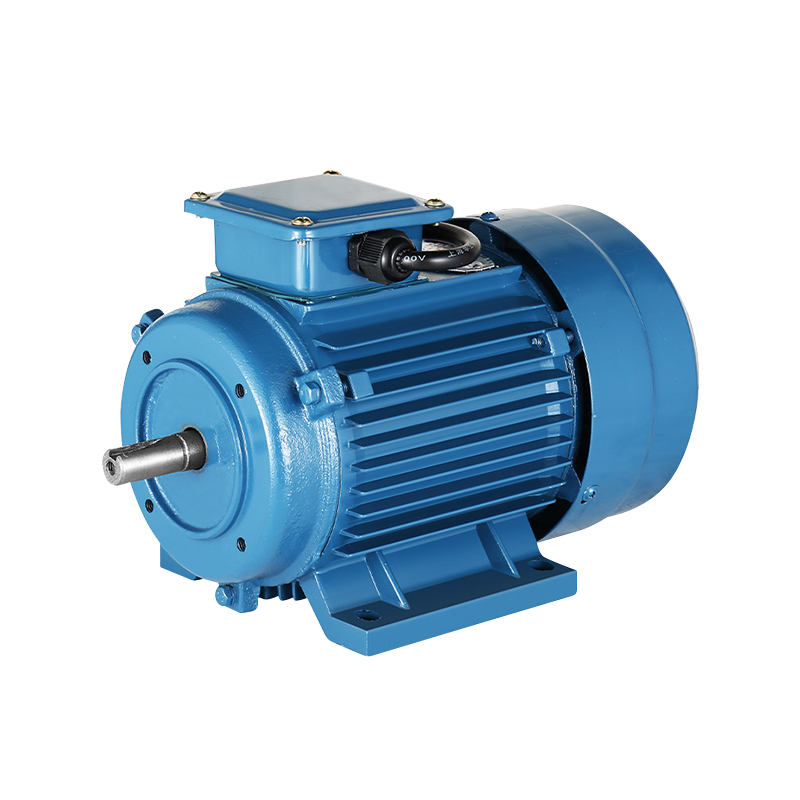
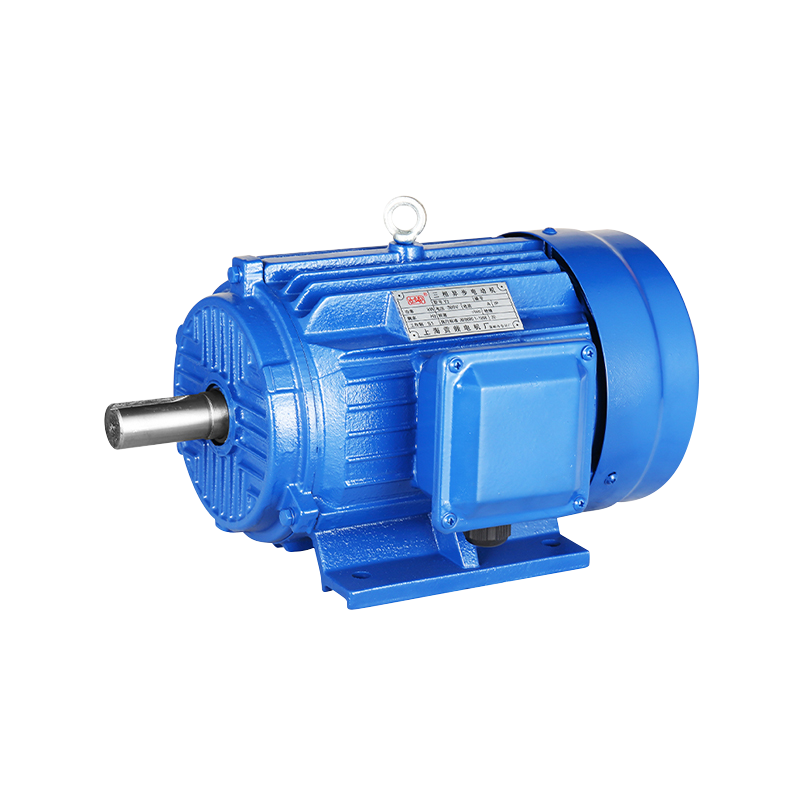
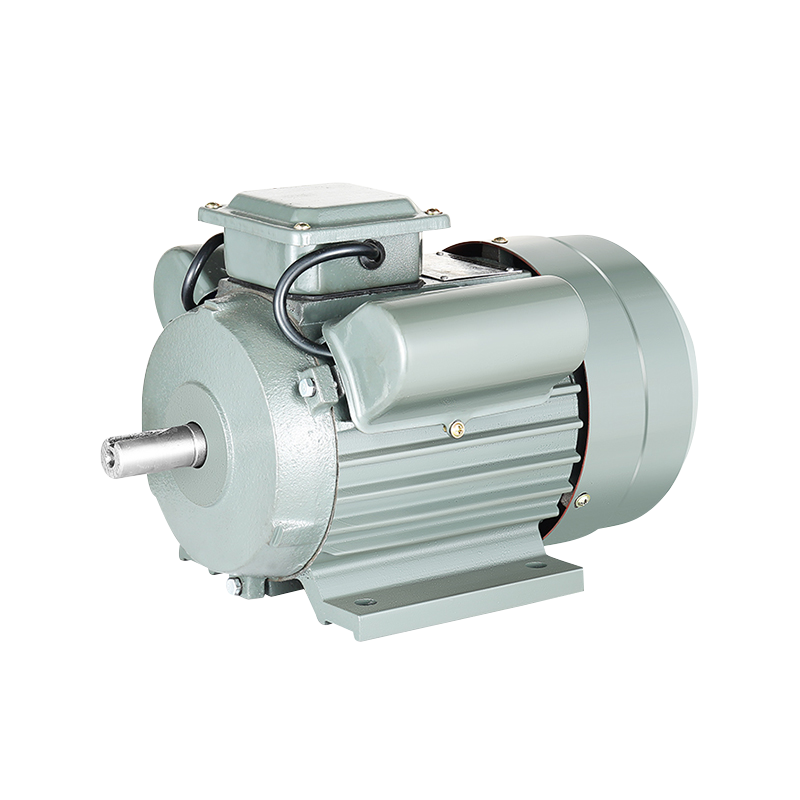
How to Properly Install a Fan Compatible Motor in Industrial Fans?
Installing a Fan Compatible Motor in industrial fans is a task that requires careful attention to detail, proper tools, and a clear understanding of both the motor’s specifications and the fan’s operating environment. A well-installed Motor ensures reliable operation, reduced maintenance, and improved efficiency in demanding industrial settings. This article will guide you through the key steps and considerations for properly installing a Fan Compatible Motor in industrial fans.
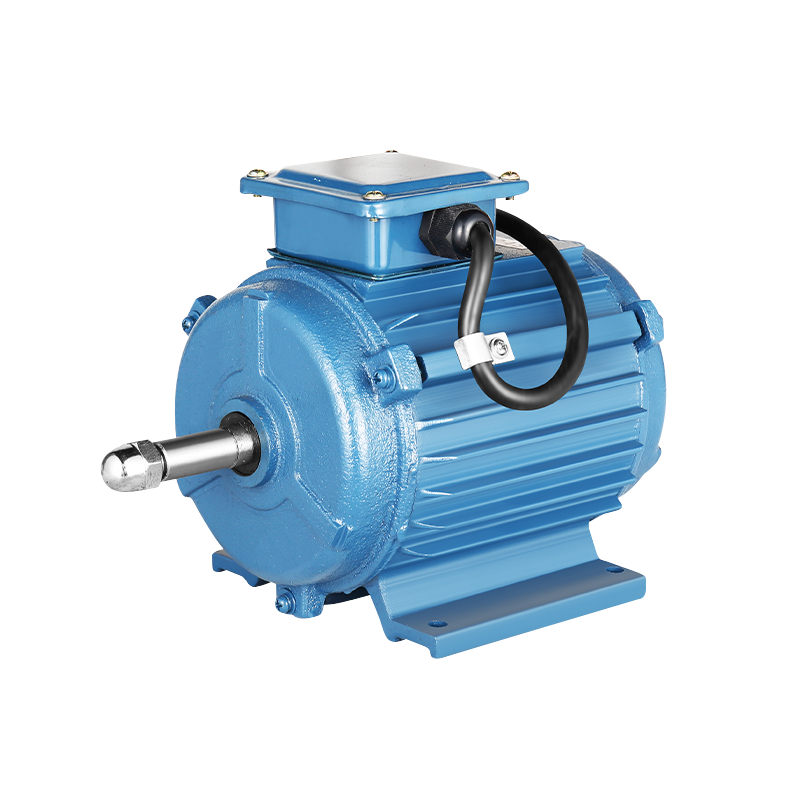

Before beginning the installation, it is essential to verify that the Fan Compatible Motor matches the specifications required for the fan. This includes checking the voltage, horsepower, speed (RPM), frame size, and shaft dimensions. Ensuring compatibility between the Compatible Motor and the fan system helps avoid operational problems and unnecessary adjustments later.
The next step is to prepare the work area. The fan and motor installation site should be clean, dry, and free from dust or debris that could interfere with the process. Position the Fan Compatible Motor close to the fan assembly and have all necessary tools, including wrenches, screwdrivers, alignment tools, and mounting hardware, ready for use.
When removing the old motor, disconnect all electrical connections safely by following lockout/tagout procedures to prevent accidental activation. Carefully unfasten the motor from its mounting base and detach it from the fan assembly. Take note of how the original Fan Compatible Motor was positioned, as this can serve as a helpful reference during installation.
Mounting the new Motor begins by aligning it with the fan’s frame and mounting holes. Use the appropriate bolts and secure the motor evenly to prevent vibrations during operation. It’s important to avoid over-tightening, as this can cause stress on the motor housing or mounting brackets. The motor shaft should be aligned precisely with the fan hub to prevent excessive wear on bearings and couplings.
Once the Fan Compatible Motor is securely mounted, attach the fan blades or impeller to the motor shaft. Make sure the connection is firm and that the fan components are balanced to reduce operational noise and vibration. If the system uses a belt drive, install the belt and adjust the tension according to the motor and fan manufacturer’s recommendations.
Electrical connections are a critical step in the installation process. Connect the Fan Compatible Motor to the power supply according to the wiring diagram provided with the motor. Double-check that the connections are secure and that the proper insulation is applied to prevent short circuits or electrical hazards. It’s also a good practice to verify the grounding of the Motor to protect against electrical faults.
Before starting the Fan Compatible Motor, rotate the fan blades by hand to ensure there’s no obstruction and that they move freely. Check all bolts, connections, and mounting points to confirm they are secure. Once satisfied, restore power and start the Motor briefly to observe its rotation direction. It should match the airflow direction required for the fan system. If the direction is incorrect, follow the motor wiring instructions to safely reverse the rotation.
After confirming the correct rotation, run the Fan Compatible Motor at operational speed and observe for any unusual noises, vibrations, or overheating. A smooth and quiet operation indicates proper alignment and installation. Monitor the motor’s performance over the next few hours to ensure it remains stable under continuous load.
Regular inspection and maintenance after installation are also important to extend the service life of a Fan Compatible Motor. Periodically check the alignment, bolt tightness, and electrical connections. Clean dust or debris from the motor housing and ventilation openings to maintain cooling and prevent overheating during operation.
Proper installation of a Fan Compatible Motor not only ensures reliable performance but also reduces downtime and repair costs in industrial operations. By following these installation practices, operators can maintain the integrity of their ventilation systems and support a safer, more efficient working environment.
-
Feedback

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体