Manual Punch Press Innovations Drive Precision Manufacturing Forward
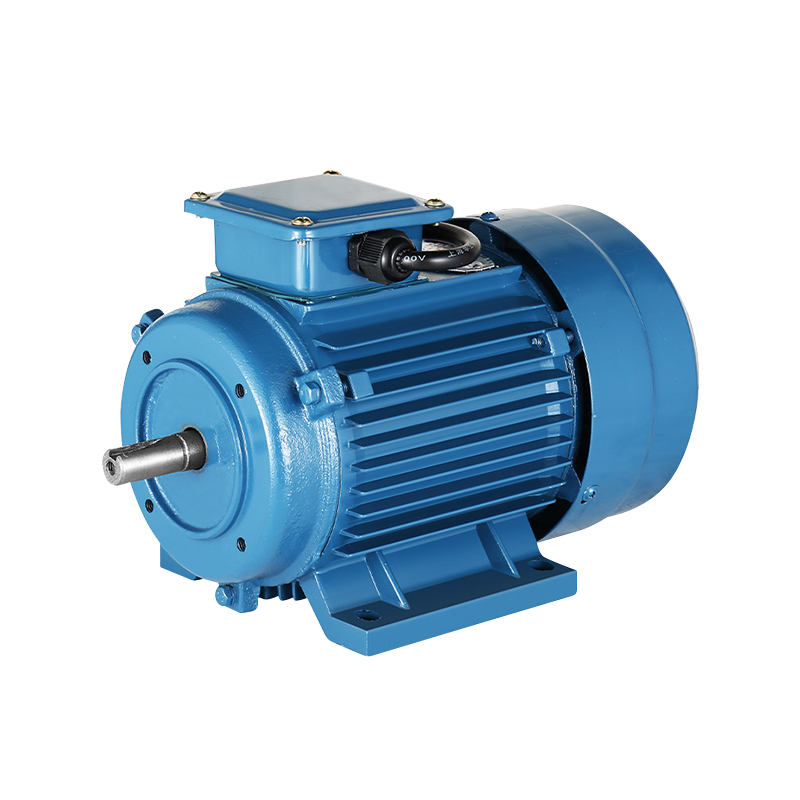
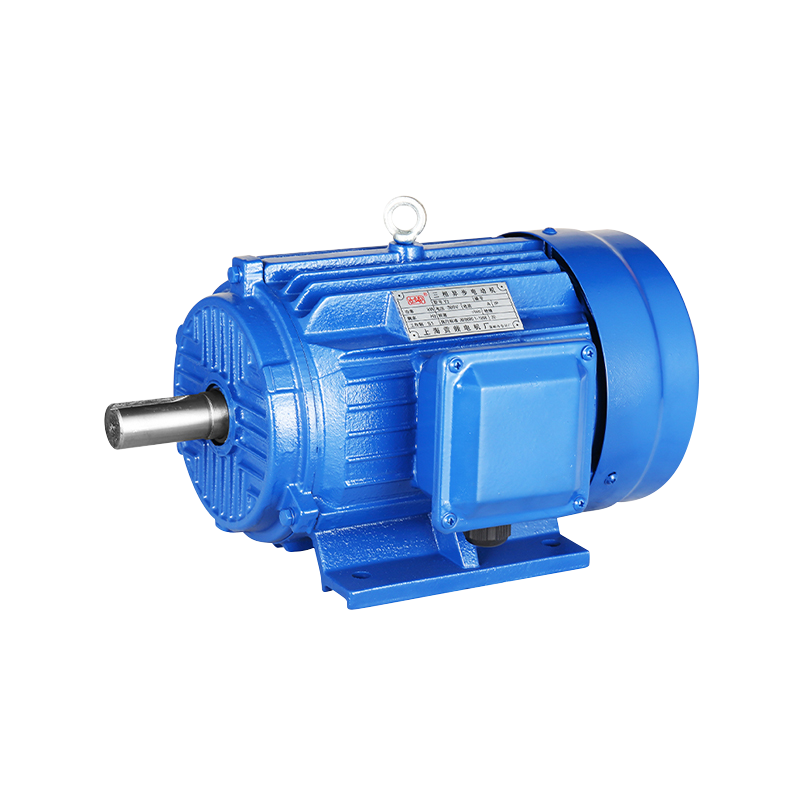
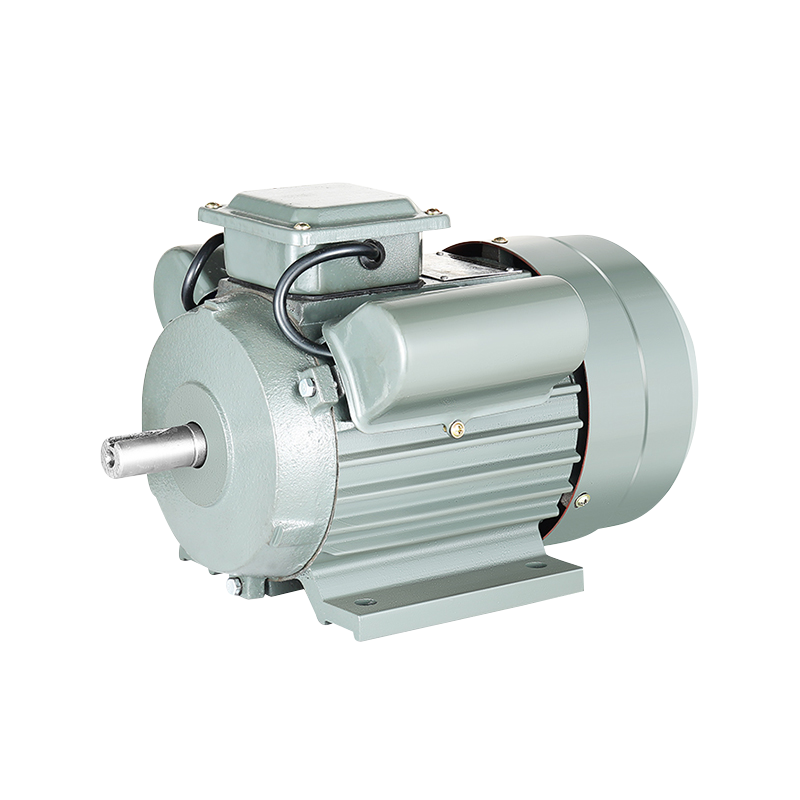
In modern manufacturing, precision and efficiency are crucial for maintaining competitive production processes. One area that has seen steady evolution is the use of the manual punch press in metalworking and fabrication environments. Over the years, advancements in design and integration with supportive machinery have allowed the manual punch press to achieve higher accuracy and flexibility while maintaining its traditional usability. Paired with technologies such as the Three-Phase Asynchronous Motor, these presses offer consistent performance and reliability, meeting the demands of a variety of industrial settings.
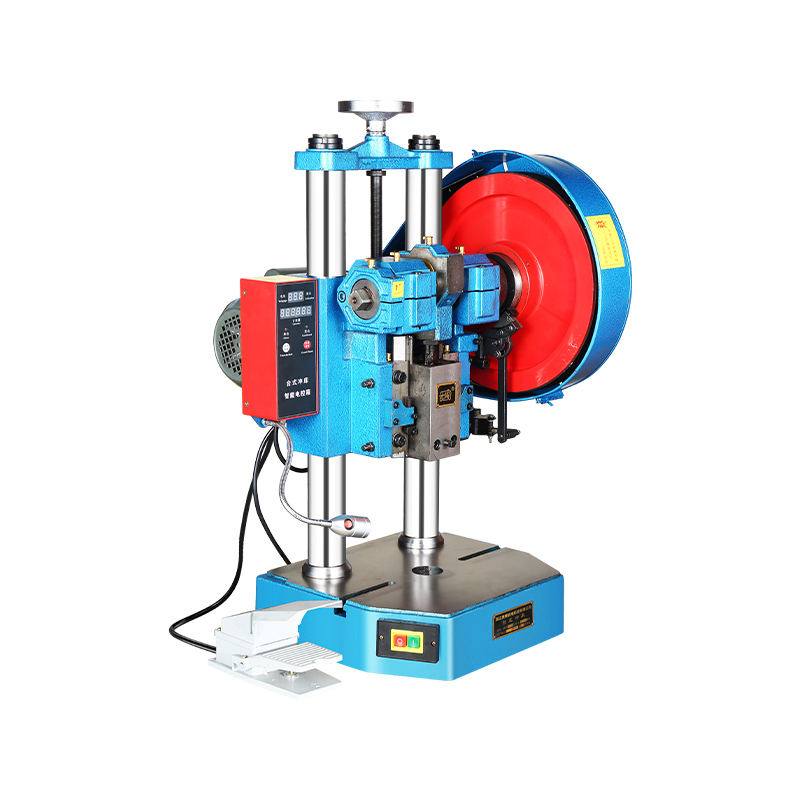

Enhancing Accuracy Through Design Improvements
The manual punch press has benefited from design enhancements that prioritize accuracy and user control. Adjustments in frame rigidity, guide alignment, and punch tooling have enabled operators to achieve tighter tolerances. These improvements allow manufacturers to handle a wider range of materials and thicknesses while less material waste. The integration of a Three-Phase Asynchronous Motor provides steady, controlled power, which complements the manual operation by reducing variations in punch speed and force. In applications where precision is essential, such as creating complex sheet metal components, this combination ensures that production outcomes remain consistent.
Versatility Across Production Tasks
One of the defining advantages of the manual punch press is its adaptability to diverse tasks. From perforating metal sheets to forming components for industrial machinery, the press can accommodate a variety of dies and tooling setups. When paired with a Three-Phase Asynchronous Motor, the manual punch press can maintain uniform motion and torque, supporting repetitive tasks without compromising quality. This versatility allows manufacturers to utilize a single machine for multiple production processes, reducing the need for specialized equipment and streamlining workflow.
Integration with Modern Manufacturing Systems
While the manual punch press remains operator-driven, integration with modern manufacturing systems has expanded its capabilities. CNC interfaces, electronic monitoring, and power-assist options have made it easier to maintain consistent results over long production runs. The Three-Phase Asynchronous Motor plays a critical role in these systems, providing reliable power for rotational or linear motion components and supporting automation where necessary. By combining traditional manual control with modern motor technology, manufacturers can achieve a balance between flexibility and efficiency, making the manual punch press a relevant tool in contemporary facilities.
Maintenance and Reliability Considerations
The durability of both the manual punch press and the Three-Phase Asynchronous Motor contributes to long-term operational stability. Routine maintenance such as lubrication, alignment checks, and motor inspections ensures that machines continue to function effectively over years of use. Additionally, the simplicity of manual punch press mechanics reduces the likelihood of complex breakdowns, while the Three-Phase Asynchronous Motor offers low-maintenance performance with steady electrical operation. Together, these elements support consistent production schedules and reduce downtime.
Impact on Production Quality and Efficiency
Innovations in manual punch press design, supported by the integration of the Three-Phase Asynchronous Motor, have a tangible impact on manufacturing quality and efficiency. Manufacturers can achieve uniform punching results, improve material utilization, and manage labor resources more effectively. In industries ranging from automotive component fabrication to custom metalwork, this combination supports precision-driven workflows without requiring a fully automated environment. The ongoing evolution of these tools demonstrates that traditional machinery can continue to advance alongside modern technologies.
The manual punch press has evolved beyond its conventional roots through design improvements, enhanced versatility, and integration with supportive technologies such as the Three-Phase Asynchronous Motor. These developments ensure that precision manufacturing can advance while maintaining reliability, flexibility, and efficiency, keeping the manual punch press relevant in a diverse range of industrial applications.
-
Feedback

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体